- The danger of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic is significant due to the rapid spread of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus two variant omicron. Despite vaccine rollouts’ continued success, the virus’s evolving mutations threaten to make battling the sickness much more difficult. This is made worse by a lack of knowledge about the omicron variant.
In this context, researchers from all around the globe are examining the behavior of the omicron variant and its origin. In a recent paper released on the preprint site bioRxiv*, Chinese researchers employed atomistic molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the complex structure of the omicron variant’s receptor-binding domain (RBD) with the human host receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recognized the new type as a VOC on November 26th, 2021, and named it (B.1.1.529) Omicron. Many mutations, particularly in spike proteins, are unheard of (which attach to the host receptor). The RBD contains 15 modifications, whereas the spike protein contains over 30. There are roughly ten mutations in the RBD binding interface to the receptor protein ACE2.
The RBD on the spike protein is necessary for infection to occur and for the host cell to enter. Because most drugs target the spike protein, it’s crucial to investigate the differences in the omicron form.
The researchers wanted to know if the RBD of the omicron variety binds closely to the ACE2 and if there is another receptor that might help infect healthy cells. The researchers obtained information on omicron mutations from the US CDC website for their investigation.
The researchers showed the SARS-CoV-2 phylogenetic tree, which has the most spike protein changes in the omicron version thus far. They also demonstrated where the receptor binding sites had been mutated, particularly around the ACE2 interaction surface.
Even in the instance of the RBDO, where alterations only minimally modify the structure relative to the wild-type, the researchers discovered that the RBD and ACE2-RBD complex structures remained stable. Depending on the root-mean-square-deviation (RMSD) of the systems, the researchers anticipated that changes in the omicron version do not significantly impair RBD stability; instead, the ACE2-RBD complex is even somewhat more stable than the wild type complex.
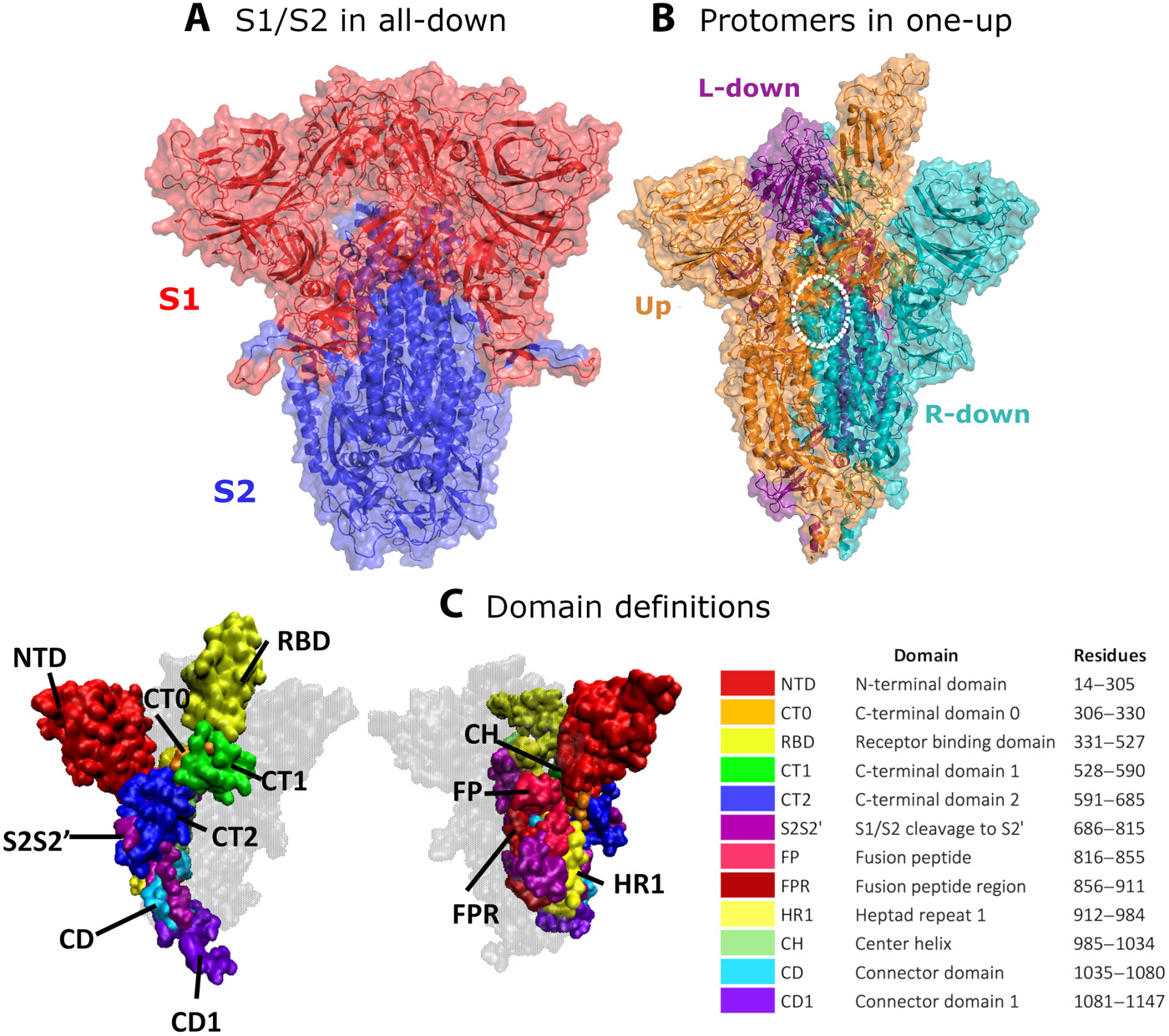
ACCORDING TO THE RESEARCHERS, the RBD is stiffer than its wild counterpart (1.5 vs. 2.1, according to the average values of the RMSF). While the 15 altered residues produced oscillations in the omicron variant compared to the wild type, the researchers believe that binding to ACE-2 stabilizes these residues, improving the ACE-2-RBD complex’s stability.
The researchers compared the hydrogen bonding between the Omicron RBD and ACE-2 to the wild-type binding and observed that the omicron version has stronger connections. The number of van der Waals connections between ACE2 and RBD and the buried surface area were estimated and graphically shown to determine the binding affinity between the two proteins.
After discussing the electrostatic potential concentrated around the mutation sites, they calculated the binding energies. Compared to the wild type, the measured data revealed a more excellent binding between ACE-2 and RBDO.
What Concerns Do You Have About The Covid 19 Variant Omicron?
Compared to current variations, there remain unsolved issues about Omicron’s contagiousness and transmissibility. Dr. Monica Mahajan tells the tale of Omicron thus far. Omicron (B.1.1.529) is a SARS-CoV-2 variant initially identified in COVID-19 individuals throughout Botswana and South Africa.
The WHO Technical Advisory Committee on Virus Evolution (TAG-VE) said the virus had too many changes and might readily spread worldwide, leading to a rise in COVID cases. TAG-VE identified it as a ‘Variant of Concern’ (VOC). The other varieties formerly labeled as VOC became known as Delta.
According to the WHO Director-General, Omicron has already been recorded in 77 nations worldwide, and it is likely prevalent in most countries even if it has not been discovered.
He believes that vaccines will not be enough to get countries out of this predicament. Vaccines against masks, social separation, ventilation, or hand hygiene are not available. We must do everything and do it consistently!
All sorts of viruses, including SARS-CoV-2, develop changes in their genetic material or genome as they replicate. During the pandemic, this virus evolved into several forms. Scientists continue to collect data on various variations worldwide by researching their DNA sequence in laboratories to determine the contagiousness and severity of disease induced by these variants.
So these variations have a similar parent or lineage that initiated the pandemic in Wuhan. Still, the virus’s properties have altered over the last two years, particularly in versions with too many mutations. The variations have been labeled using Greek alphabets. These have ramifications in diagnosis, treatment, immunization, and prevention methods.
What is the significance of Omicron being designated as a Variant of Concern?
Omicron is known as a VOC because the spike protein contains many mutations and substitutions, and it has supplanted the Delta version in South Africa. Not only that but it’s been seen in a variety of nations throughout the world, even in people who had no prior travel experience. It might be more resistant to vaccine-induced protection and therapies, such as monoclonal antibodies, that are now available. Scientists are currently accumulating information on the disease’s disease transmission and lethality.
Compared to current variations, there remain unsolved issues about Omicron’s contagiousness and transmissibility. To address this riddle, epidemiologists analyze data from South Africa and other countries across the world.
The second and more pressing question concerns the degree of Omicron-induced sickness. According to preliminary data, the virus is infecting younger people, although the condition is milder. Other versions exhibit symptoms that are highly similar to this one. In the following months, a far clearer picture will emerge. All COVID-19 variations can cause significant sickness and death in sensitive people, especially those with co-morbidities, so we must still be exceedingly cautious.
Is it possible that we have a potential edge over other nations since so many Indians have experienced the sickness and more than half of our population has been vaccinated? We’re getting preliminary data on vaccinations from Pfizer and Astra Zeneca/Covishield, with mixed outcomes.
Finally, do more sensitive and specific diagnostic tests need to be developed to check the disease early? Will the existing test kits detect the COVID-19 variations?
The extensively mutated Omicron is a mystery and undoubtedly a Variant Of Concern at this point, with so many unknowns. In the meantime, protective measures, including masks, social separation, and hand cleanliness, remain our best bets. In our worldwide effort to combat the pandemic, government agencies must strengthen monitoring, improve public health measures, and share information via database platforms.
Also Read: Researchers have discovered a Relationship between asthma and brain tumors